
Remember the time when hospital wards were flooding with patients? Yes! We all know it- The covid time- A time when patient population was increasing in every hospital across the world which made patient care a herculean task for all the doctors and nurses.
Now, imagine, if every hospital is full, leaving no room for new admissions, how and where would the doctors & nurses attend to every new patient amidst the chaos? To put a full-stop to this chaos, it is essential to look into the number of readmissions in the hospital- the reason behind it and the frequency of it. This is where AI comes to rescue- Leveraging AI Development to manage readmissions is the smartest option that experts out there came up with!
Before diving deep into how AI can transform patient care with its rare and rational insights, it is important to understand the common factors that lead to readmissions.
Top Reasons for clinical readmission
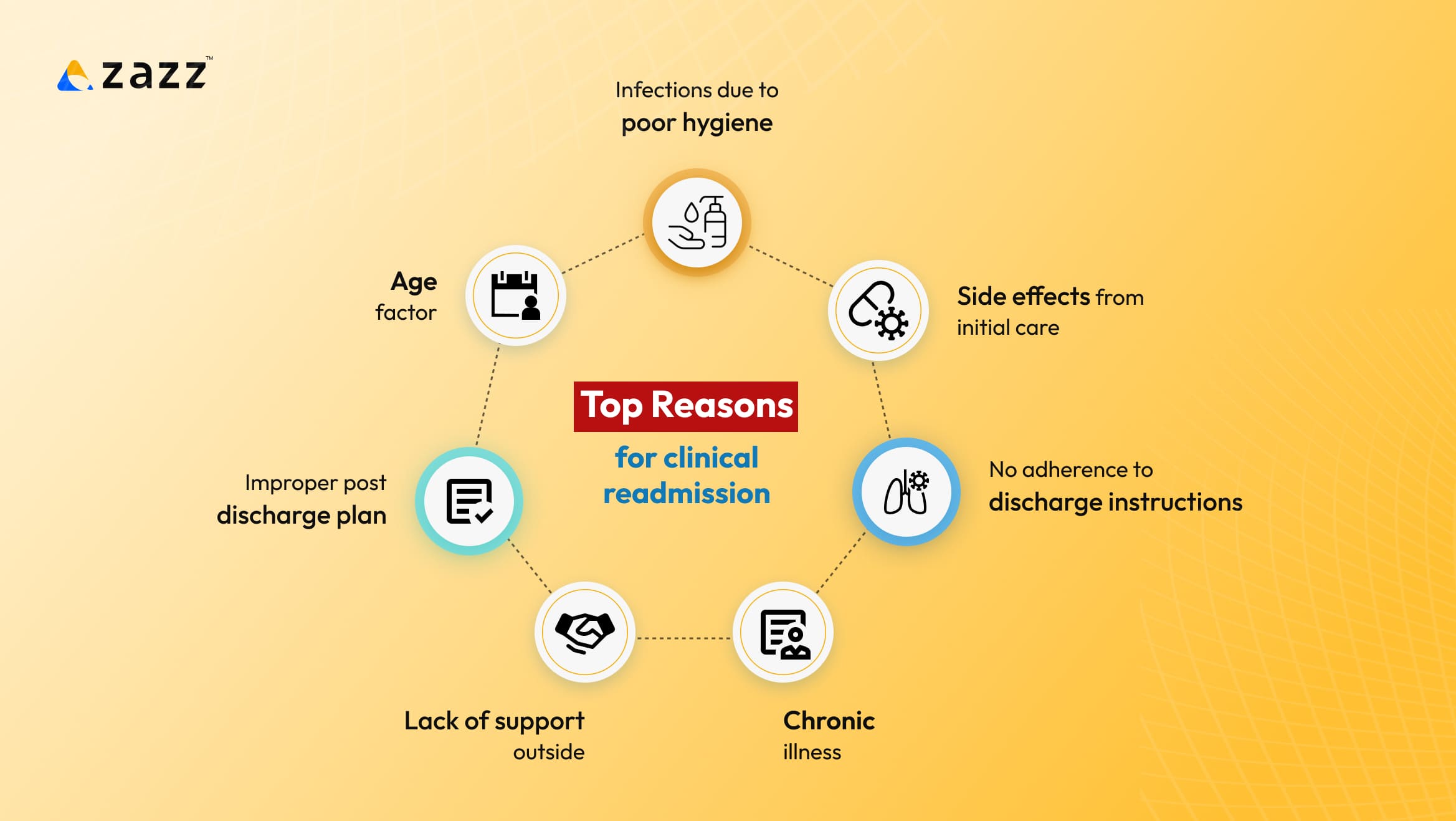
1. Chronic illness:
Patients dealing with chronic illness such as cancer, diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, COPD etc., may have unprecedented complications in which case readmission is inevitable.
2. No adherence to discharge instructions:
The indifference from the patients’ side in being regular with the medications or following the care for cure as instructed by the practitioners, are some of the common reasons that lead to readmissions.
3. Side effects from initial care:
Some medications might not suit a few patients- i.e., their body might be intolerant to some of the ingredients used in the medication. Incase of adverse effects, patients may be readmitted for further observation.
4. Infections due to poor hygiene:
There are chances for hospitalized patients to contract an infection due to either poor personal hygiene or poor environmental hygiene during or after hospitalization. In both the scenarios, patients will be subjected to readmission for prolonged care.
5. Age factor:
Patients who are 50 & above are prone to comorbidities & they may have to deal with recurrence of complications or higher severity of complications which can be brought under control only by intensive post-discharge support which includes readmissions when necessary.
6. Improper post discharge plan:
Lack of appropriate discharge instruction and insufficient follow ups post discharge can leave the patient confused, making them do things on their own without clarity eventually leading them to readmission.
7. Lack of support outside:
Some patients might lack support from their primary circle for timely care & speedy recovery. Such patients tend to rely on hospitals everytime incase of complications as they do not have moral support at home.
Related reading: Top 10 Benefits Of Mobile Apps In Healthcare Industry
The above are some of the most common reasons that increase readmissions in hospitals. Now, this might trigger another question, “Why is it important to reduce readmission in hospitals?” Here is why
- Patient safety: High readmission rates can risk patients’ safety. When patient safety is compromised either due to poor monitoring or poor care, it might lead to more complications resulting in worse outcomes
- Effective resource utilization: The resource capacity of a hospital is invariably limited both in terms of manpower and in terms of technology. Giving the resources more than what they could handle will strain them, resulting in inadequate patient care.
- Hospital reputation: The more a patient keeps coming back, the more problematic it is for the hospitals. Hospitals may face penalties from insurers for high readmission rates, which can also impact their reputation and accreditation status.
- Patient experience: From a patient’s point of view, readmission is not something they would prefer personally. So, when situations arise for readmission, it will make them question the care, giving them a bitter experience overall.
- Healthcare Costs: Readmissions contribute to increased healthcare costs for both patients and the healthcare system, often resulting in unnecessary expenses and resource use.
- Better care management: Focusing on reducing readmissions encourages better communication and coordination among healthcare providers, enhancing overall patient care.
- Health Disparities: Addressing the causes of readmissions can help reduce health disparities among vulnerable populations who may be disproportionately affected.
Now, with the help of AI hospital readmissions can be significantly reduced. Here’s how.
Related reading: Top 5 Healthcare Mobile App Features in 2024
How is AI helpful in reducing readmission in hospitals?

Predictive Analytics:
AI algorithms can analyze patient data to identify individuals at high risk of readmission. By examining factors such as demographics, medical history, and treatment plans, AI can help healthcare providers target interventions effectively. Natural Language Processing (NLP) can analyze patient notes and discharge summaries to identify concerns or risks that might lead to readmission, facilitating better follow-up care and communication.
Personalized Care Plans:
AI can assist in creating tailored discharge plans that consider individual patient needs, preferences, and social determinants of health, improving adherence to post-discharge care.AI can streamline communication between different care teams, ensuring that all providers are informed about a patient’s care plan and needs, reducing gaps in care.
Remote Monitoring:
AI-powered wearable devices and telehealth solutions can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs and health conditions post-discharge, alerting healthcare providers of potential issues before they require readmission. AI driven Patient Engagement Tools like tab reminders, tele assistants can enhance patient engagement by reminding them about medications, follow-up appointments, and self-care practices, improving adherence to treatment plans.
Effective Resource Allocation:
AI can optimize staffing and resource allocation in hospitals, ensuring that high-risk patients receive adequate support and monitoring during their stay, so that there will be no necessity for further readmissions. AI also can recommend appropriate interventions with real-time decision support tools that help identify potential complications, thus reducing the likelihood of readmission.
By leveraging these AI capabilities, healthcare systems can enhance patient outcomes, improve care transitions, and ultimately reduce the rates of hospital readmissions.
Related reading: What Is Interoperability in Healthcare? Complete Guide
Conclusion:
AI is certainly a boon if used the right way. With the growing clinical needs, it is important to focus on tackling high readmission rates. Given the fact that AI can play a significant role in effectively reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes, healthcare organizations should proactively engage with AI to level up patient care and achieve the best outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
It certainly can with predictive analysis, NLP (natural language processing) & other decision support tools.
Hospitals may face penalties from insurers for high readmission rates, which can also impact their reputation and accreditation status.
AI-powered wearable devices and telehealth solutions can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs and health conditions post-discharge, alerting healthcare providers of potential issues before they require readmission. AI driven Patient Engagement Tools like tab reminders, tele assistants can enhance patient engagement by reminding them about medications, follow-up appointments, and self-care practices, improving adherence to treatment plans.
It can predict potential diseases & risks in patients. It can improve operational efficiency by helping in effective resource allocation. By analyzing historical data, predictive models can suggest personalized treatment plans based on patient characteristics and expected outcomes.
Chronic illness, side effects from initial care, age factor, lack of support from primary circle, improper discharge plan, infections due to poor personal or environmental hygiene in or outside hospital and no adherence to post-discharge instructions.
Recent Articles
Table of Content 1. Data Engineer vs. Data Scientist: Understanding...
Table of Content 1. What is the Carnival in Brazil?...
Table of Content 1. What is IT Staff Augmentation? 2....












