
In recent years, the healthcare sector has seen a remarkable transformation, primarily driven by the advent of technology. Among the many technological advancements, Electronic Health Records (EHR) and medical record automation stand out for their ability to improve patient care, streamline administrative tasks, and enhance overall healthcare efficiency. One of the key components of this transformation is the implementation of automated medical record systems, which have changed how patient information is stored, tracked, and managed.
This blog will delve into the significance of EHR and medical record automation, exploring its benefits, the role of automated medical record tracking systems, and how the integration of technology in medical records has improved healthcare delivery and operational performance.
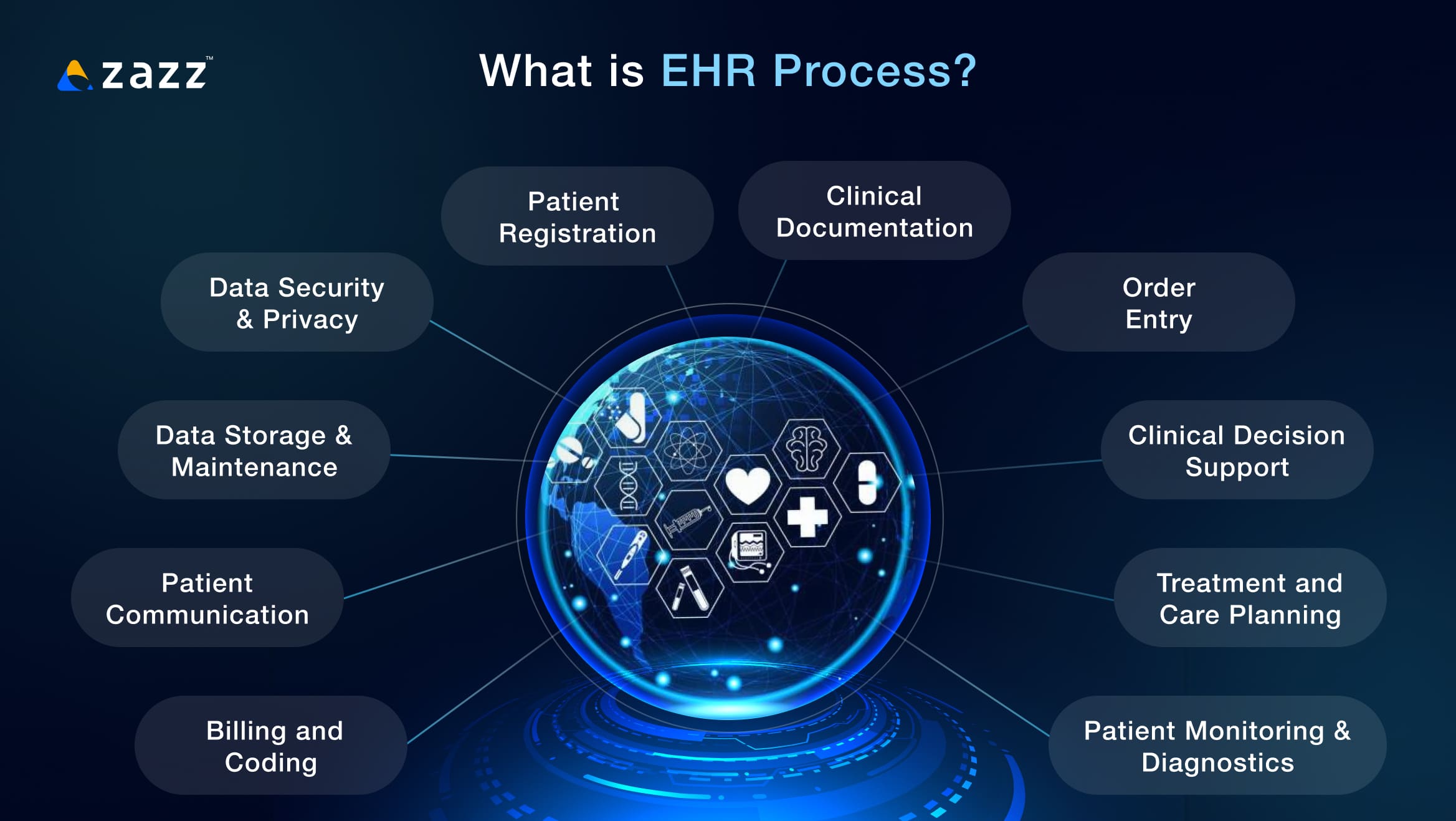
What is EHR process?
EHR (Electronic Health Record) process refers to the systematic use and management of patient health information in digital form. An EHR is an electronic version of a patient’s medical history, including key clinical data such as diagnoses, medications, lab results, treatment plans, and other relevant health information. It is designed to be shared across different healthcare providers, improving the quality of care and making it easier for healthcare professionals to access a patient’s health information.
Here’s a breakdown of the typical EHR process:
1. Patient Registration
- Initial Data Entry: When a patient visits a healthcare provider for the first time, their personal information, such as name, address, contact details, insurance information, and medical history, is entered into the EHR system.
- Demographic Information: The system records the patient’s age, gender, ethnicity, and other demographic details that are important for their care.
2. Clinical Documentation
- Encounter Notes: During each visit or consultation, healthcare providers record patient information, such as symptoms, medical history, physical exam findings, diagnoses, and treatment plans. These records are stored digitally in the EHR system.
- Medical History: Physicians document relevant patient history such as past illnesses, surgeries, allergies, vaccinations, and family medical history.
3. Order Entry
- Orders for Tests/Medications: EHRs allow healthcare providers to place orders for laboratory tests, imaging, medications, and other treatments electronically. This reduces the risk of errors associated with handwritten orders and improves coordination among healthcare teams.
- Prescription Management: Prescriptions are generated electronically through the EHR system, which can be sent directly to pharmacies. It helps in reducing medication errors and streamlining the prescription process.
4. Clinical Decision Support
- Alerts and Reminders: The EHR system provides real-time alerts for things like medication interactions, allergies, missed vaccinations, or abnormal lab results. This helps clinicians make informed decisions and avoid potential issues.
- Evidence-Based Guidelines: EHRs often incorporate clinical guidelines and best practices to support decision-making, helping to standardize care and improve outcomes.
5. Patient Monitoring and Diagnostics
- Integration with Devices: Many modern EHR systems integrate with monitoring devices such as blood pressure cuffs, glucose meters, and ECG machines, allowing healthcare providers to track a patient’s health status in real time.
- Lab Results and Imaging: Lab results and diagnostic images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs) are stored and accessed within the EHR system, enabling timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment.
6. Treatment and Care Planning
- Developing Care Plans: Based on the patient’s health information, healthcare providers create treatment plans that include medications, therapy, follow-up care, and lifestyle recommendations.
- Collaboration with Specialists: When a patient needs specialized care, the EHR allows providers to share relevant health data with specialists, ensuring comprehensive and coordinated treatment.
Related reading: How to Build an EHR System: A Comprehensive Guide
7. Billing and Coding
- Medical Billing: EHRs often include coding and billing features, where providers can select codes for diagnoses, procedures, and treatments. This helps in generating accurate bills for insurance claims and patient payments.
- Insurance Claims: The system can directly send claims to insurance companies for reimbursement, reducing delays and errors.
8. Patient Communication
- Patient Portal: Many EHR systems offer patient portals, where patients can access their health records, view lab results, schedule appointments, request prescription refills, and communicate securely with their healthcare providers.
- Follow-Up Reminders: EHRs can send automated reminders to patients about upcoming appointments, necessary screenings, vaccinations, or follow-up care.
9. Data Analysis and Reporting
- Clinical Analytics: EHRs allow healthcare organizations to analyze patient data in aggregate, identifying trends in patient populations, disease outbreaks, and care outcomes.
- Quality Reporting: EHR systems often support reporting requirements for government development programs, insurance companies, and regulatory bodies, allowing healthcare providers to demonstrate quality care.
10. Data Security and Privacy
- Access Controls: EHR systems have strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can view or modify patient data.
- Compliance with Regulations: EHR systems are designed to comply with healthcare data security regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States, ensuring that patient data is kept private and secure.
11. Interoperability and Data Sharing
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): EHR systems facilitate the sharing of patient information between different healthcare providers and organizations, allowing for better-coordinated care, especially when patients see multiple specialists or are treated in different locations.
- External Integration: EHRs may integrate with external databases, insurance companies, pharmacies, and public health organizations to streamline processes and improve overall care delivery.
12. Data Storage and Maintenance
- Long-Term Storage: EHRs provide a secure, digital repository for a patient’s entire health history, making it easier to maintain and retrieve medical records over time.
- Updates and Maintenance: The system is regularly updated with new health information, and it must be maintained to ensure that it remains accurate and up to date.
In summary, the EHR process is designed to streamline and enhance the management of patient data, improve communication between healthcare providers, reduce errors, and increase the efficiency and quality of care. By digitizing medical records, the process also enables more effective decision-making and better coordination across healthcare teams.
What processes in EHR can be automated?
In Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, many processes can be automated to improve efficiency, reduce errors, enhance patient care, and streamline administrative tasks. Below are key processes within EHR that can be automated:
1. Patient Registration and Data Entry
- Automated Patient Data Capture: Automation tools can pre-fill patient demographic data from previous visits, insurance providers, or external databases to reduce manual entry.
- Self-Registration: Patient portals or kiosks can allow patients to update or verify their personal information automatically before their visit, ensuring data accuracy and reducing administrative burden.
- Automated Data Validation: EHRs can automatically verify entered patient data (such as insurance information or medications) against external databases to ensure accuracy and completeness.
2. Clinical Documentation
- Speech Recognition: Systems like Dragon Medical or M*Modal allow healthcare providers to dictate patient notes, which are automatically transcribed into the EHR.
- Templates and Smart Forms: Automated templates and smart forms can auto-populate sections of the patient’s chart based on predefined conditions or previous visits, reducing repetitive data entry.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP can be used to extract key information from unstructured text (e.g., doctor’s notes) and convert it into structured data within the EHR, improving accessibility and analysis.
3. Order Entry (CPOE – Computerized Physician Order Entry)
- Automated Test Orders: EHR systems can automatically generate lab or imaging test orders based on clinical documentation, such as symptoms or diagnoses entered by the clinician.
- E-Prescribing: Medication prescriptions can be automatically generated and sent to pharmacies electronically, reducing errors related to handwriting or manual data entry.
- Order Approval Workflow: Automated approval processes for clinical orders, such as medication dosages or medical procedures, can ensure that proper clinical review is carried out.
Related reading: 15 Best EHR Features in a List
4. Clinical Decision Support
- Real-Time Alerts and Reminders: EHRs can automate the process of sending real-time alerts for medication interactions, allergies, abnormal lab results, preventative screenings, or critical care reminders.
- Guideline Automation: The system can automatically suggest clinical guidelines or best practices based on the patient’s diagnosis and medical history, aiding in treatment planning.
- Risk Stratification: EHRs can use algorithms to automate the identification of high-risk patients based on predefined criteria (e.g., age, medical history, comorbidities).
5. Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
- Automated Scheduling: EHRs can integrate with scheduling systems to automatically book patient appointments based on clinician availability, reducing the risk of human error and double-booking.
- Automated Appointment Reminders: Patients can receive automated reminders via text, email, or phone call to confirm, cancel, or reschedule appointments, reducing no-show rates.
- Follow-up Appointments: EHR systems can automatically schedule follow-up visits based on treatment plans or clinical guidelines, ensuring timely patient care.
6. Billing and Coding Automation
- ICD and CPT Code Assignment: EHR systems can automatically suggest the correct diagnosis (ICD-10) and procedure (CPT) codes based on clinician documentation, reducing the time spent on manual coding and improving accuracy.
- Billing Generation: Once coding is complete, EHRs can automatically generate bills for patients and insurance companies based on the entered codes, simplifying the revenue cycle management process.
- Insurance Claim Submission: Automated systems can submit insurance claims directly to payers, check claim status, and track the reimbursement process, reducing administrative overhead.
7. Patient Data Sharing and Interoperability
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): EHR systems can automate the secure exchange of patient data between different healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care, especially in cases where patients are referred or require multiple specialists.
- Data Transfer to Pharmacies: EHRs can automatically send prescriptions, medication histories, and lab results to pharmacies, reducing medication errors and improving patient safety.
- Automated Referral Management: EHRs can manage and automate the process of referring patients to specialists, ensuring that referrals are tracked, scheduled, and followed up.
8. Patient Communication
- Patient Portal: Automating access to patient portals enables patients to review their medical records, request prescription refills, communicate with their healthcare providers, and schedule appointments without direct involvement from administrative staff.
- Automated Follow-Up Messaging: After an appointment or procedure, patients can receive automated messages with instructions, prescriptions, or necessary follow-up actions.
- Secure Messaging: Automated secure messaging systems within the EHR allow healthcare providers and patients to communicate securely, share test results, or discuss treatment plans.
9. Automated Reporting and Analytics
- Clinical Reporting: EHRs can automate the generation of clinical reports based on real-time data, helping healthcare organizations monitor patient outcomes, track disease trends, and manage quality metrics.
- Regulatory Reporting: Automated reports can be generated for regulatory compliance purposes, such as Meaningful Use (MU), MIPS (Merit-based Incentive Payment System), or quality reporting for insurance reimbursement.
- Population Health Management: Automated population health tools analyze patient data to identify at-risk individuals, monitor care gaps, and automate follow-up care reminders for preventive measures.
10. Data Security and Compliance Automation
- Audit Trails: EHR systems can automatically log and maintain audit trails of every access or modification made to patient records, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Automated Backups: Data backups are automated, ensuring that patient records are safely stored and can be restored in case of system failure or disaster.
- Security Alerts: EHRs can automatically detect unusual access patterns or potential breaches, triggering alerts for immediate action and protecting patient privacy.
11. Medication Management
- Medication Refill Requests: Patients can submit refill requests through a portal, which are automatically processed and reviewed by healthcare providers before being sent to the pharmacy.
- Medication Reconciliation: EHRs can automate medication reconciliation by checking and updating a patient’s medication list, ensuring that all medications prescribed are accurately documented across different care settings.
12. Clinical Workflow Management
- Task Assignment: EHR systems can automatically assign tasks to relevant staff, such as processing lab results, scheduling tests, or following up with patients.
- Patient Flow Management: Automation tools can track patient movement throughout their care journey, such as scheduling appointments, monitoring wait times, and ensuring timely care delivery.
- Clinical Documentation and Review: Documentation that requires review (e.g., test results) can be automatically flagged for clinician review, helping to streamline clinical workflows and improve response time.
13. Clinical Trial Management
- Patient Eligibility Screening: EHR systems can automatically identify eligible patients for clinical trials based on pre-defined criteria, ensuring that trial recruitment is more efficient.
- Data Collection for Trials: EHR systems can automate the collection of patient data required for clinical trials, making it easier to track outcomes and patient participation.
Related reading: EMR/EHR Interface:15 Key Principles for User-Friendly Design
Benefits of Automating EHR Processes:
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces the need for manual data entry and paperwork, streamlining workflows and reducing overhead costs.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated systems can help prevent errors in coding, billing, medication orders, and clinical documentation, ensuring better patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: Automation helps with faster appointments, quick follow-ups, and smoother communication, improving patient satisfaction.
- Compliance and Security: Automation ensures regulatory compliance and enhances data security by tracking access and protecting patient information.
By automating these processes, healthcare providers can focus more on patient care, improve operational efficiency, and reduce administrative burden. It also enables better data management and supports the transition to more efficient, patient-centered care models.
Popular EHR Automation Solutions and Tools:
- Epic Systems: Offers comprehensive EHR automation features including automated alerts, billing, and documentation tools.
- Cerner: Provides automation tools in areas like patient scheduling, clinical documentation, and data analysis.
- Allscripts: Features workflow automation, interoperability, and data integration capabilities.
- Athenahealth: Offers cloud-based EHR automation solutions that streamline clinical and administrative tasks.
- eClinicalWorks: Provides a full suite of EHR and practice management tools with a focus on automating workflows and improving patient care.
The Need for EHR and Medical Record Automation
Before the introduction of EHR systems, healthcare facilities relied heavily on paper records, which were often disorganized, prone to errors, and challenging to manage. The need for a more efficient, accurate, and accessible system led to the development of EHR and medical record automation. By transitioning from paper-based systems to digital platforms, healthcare providers could automate many of the time-consuming tasks associated with record-keeping.
The integration of automated medical records into healthcare practices has allowed for improved patient care and a significant reduction in administrative burden. Medical record automation not only enhances the accuracy of patient data but also ensures that healthcare professionals have immediate access to critical information, thus facilitating more informed decision-making.
Key Benefits of EHR and Medical Record Automation
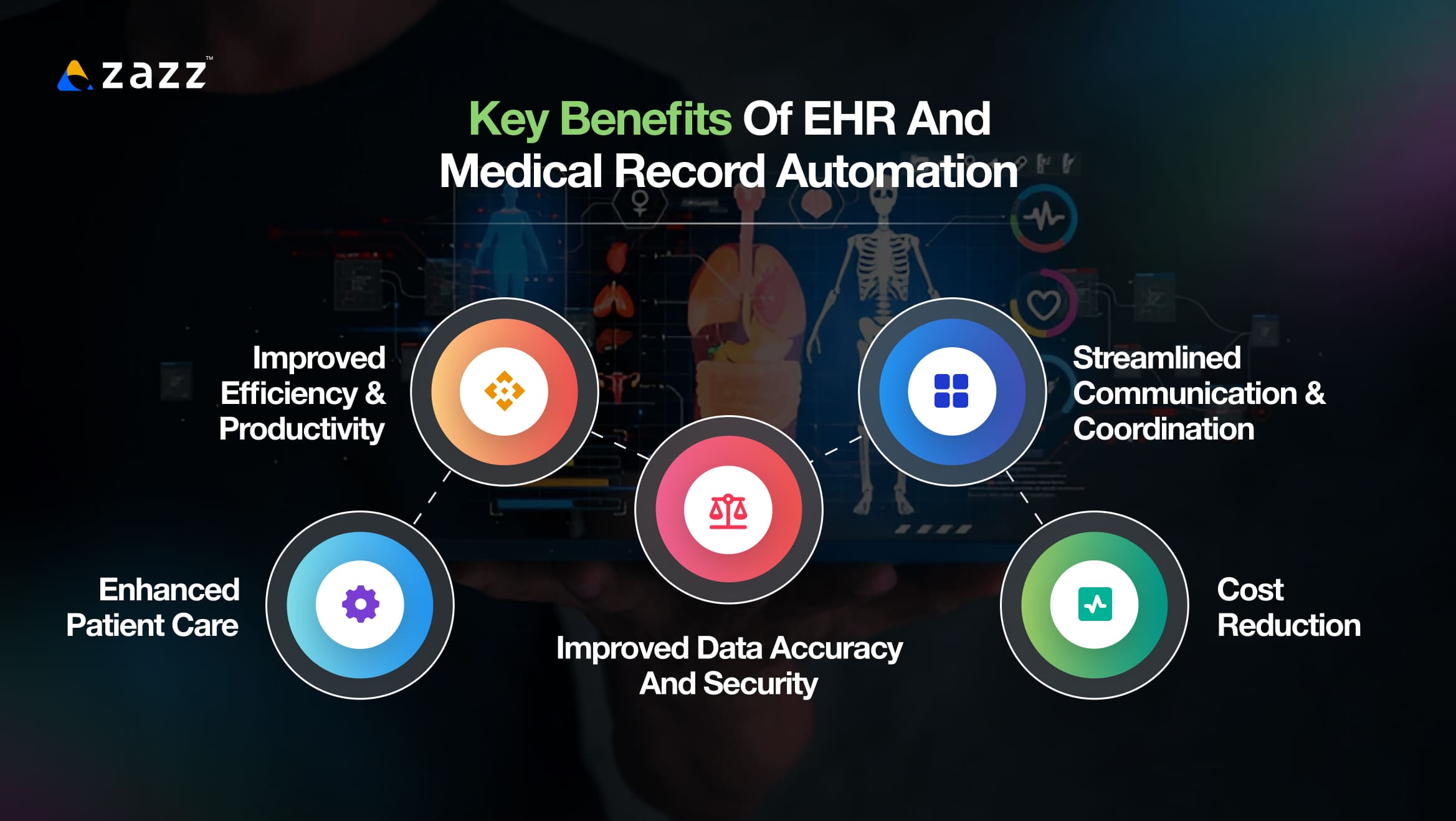
The implementation of EHR and medical record automation brings about a variety of benefits to healthcare providers, patients, and the overall healthcare system. These benefits can be grouped into several key areas:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Manual record-keeping is time-consuming and prone to human error. With automated medical record systems, healthcare workers no longer have to sift through piles of paperwork to find patient information. Instead, they can access up-to-date medical records with a few clicks. This medical record automation dramatically increases the efficiency of healthcare operations, allowing practitioners to focus on patient care rather than administrative tasks.
Moreover, EHR system automation ensures that patient data is entered once, reducing redundancy and preventing data entry errors. Automated systems can also automatically update patient records whenever new data is added, ensuring the information is always current and accurate.
2. Enhanced Patient Care
One of the most significant advantages of medical record automation is its impact on patient care. With automated systems, healthcare providers can access comprehensive patient records, including medical histories, lab results, allergies, medications, and treatment plans. This immediate access to information empowers doctors to make quicker, more informed decisions.
Additionally, automated medical record tracking systems improve patient safety by reducing the risk of medication errors, misdiagnoses, and treatment delays. With features such as alerts for allergies, drug interactions, or missing information, these systems act as a safeguard for patients, ensuring that all necessary information is considered before any medical decisions are made.
3. Improved Data Accuracy and Security
In traditional paper-based systems, the risk of human error, lost files, or illegible handwriting was a constant concern. With automated medical record systems, these issues are virtually eliminated. By automating data entry, there is less room for errors, ensuring the accuracy of patient information.
Moreover, EHR systems offer better security compared to paper records. Medical record automation systems often include advanced encryption protocols, access controls, and audit trails, which protect sensitive patient data from unauthorized access and potential breaches. This level of security is essential in maintaining patient privacy and complying with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
4. Streamlined Communication and Coordination
Healthcare often involves multiple providers working together to deliver care, and communication is key to ensuring seamless treatment. Automated medical record tracking systems enhance communication among different healthcare professionals by making patient information easily accessible in real-time.
For example, a specialist in one hospital can instantly access a patient’s medical history from a primary care physician’s office, reducing the need for redundant tests and improving the overall coordination of care. Medical record automation simplifies this process by making information easily shareable between different departments, reducing delays and enhancing collaboration.
5. Cost Reduction
Although the initial investment in EHR and medical record automation can be significant, the long-term savings are substantial. By reducing administrative tasks, improving data accuracy, and preventing redundant tests and procedures, healthcare providers can reduce overhead costs. Additionally, automated systems help eliminate the need for physical storage space for paper records, which can be costly and difficult to manage.
Hospitals and clinics also benefit from automated medical record systems by improving their billing processes. Automated billing functions reduce errors and speed up claim processing, which in turn improves cash flow and revenue cycles.
Related reading: Software Architecture for Healthcare Apps
The Role of Automated Medical Record Tracking Systems
Automated medical record tracking systems are an essential component of EHR and medical record automation. These systems are designed to track and monitor patient records, ensuring that they are organized, up-to-date, and easy to retrieve. By automating the tracking process, these systems minimize the risk of lost or misplaced records, improving the overall efficiency of healthcare facilities.
These systems work by creating a digital trail of all patient data, including appointments, treatments, lab results, and prescriptions. Every time an update is made, the system logs the change and updates the record accordingly. This automated tracking ensures that all relevant information is included in the patient’s file and is available for review by healthcare professionals at any time.
Furthermore, automated medical record tracking systems can integrate with other hospital systems, such as lab equipment or pharmacy management systems, ensuring that all aspects of patient care are seamlessly connected. This integration allows healthcare providers to view a complete picture of the patient’s health, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
EHR System Automation: The Future of Healthcare
As technology continues to evolve, the future of EHR and medical record automation looks even more promising. One of the most exciting developments is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into automated medical record systems. These technologies are enhancing the capabilities of EHR systems by enabling them to predict patient needs, suggest treatment options, and identify potential risks based on historical data.
For example, AI algorithms can analyze medical records to identify patterns that might be indicative of emerging health conditions. This predictive capability allows for early intervention, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. In addition, ML algorithms can learn from patient data, making the system even smarter over time.
Another exciting advancement in EHR system automation is the use of blockchain technology to further secure medical records. Blockchain’s decentralized nature offers an additional layer of security by making it almost impossible for unauthorized users to alter or access sensitive patient data. This added security could be pivotal in protecting against data breaches and ensuring that patient information remains private.
Overcoming Challenges in Medical Record Automation
Despite the many benefits of medical record automation, there are still challenges that healthcare organizations must address in order to fully leverage the potential of automated medical record systems. One of the most significant hurdles is the high cost of implementation. Transitioning from a paper-based system to an automated one requires considerable investment in both software and hardware. For smaller healthcare providers, this can be a financial strain.
Additionally, healthcare professionals must undergo proper training to effectively use automated medical record tracking systems. Inadequate training can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and resistance to the new system. Ensuring that staff is well-versed in using EHR systems is critical for successful adoption.
Another challenge is ensuring interoperability between different EHR systems. With multiple healthcare organizations using different systems, seamless data sharing can become a challenge. However, efforts are being made to standardize EHR systems and improve interoperability to ensure that patient data can be shared across different platforms.
Related reading: What Is Interoperability in Healthcare? Complete Guide
Conclusion
The implementation of EHR and medical record automation has had a profound impact on the healthcare industry. By improving efficiency, enhancing patient care, and reducing costs, automated medical record systems have become a cornerstone of modern healthcare. The integration of automated medical record tracking systems has further streamlined processes, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care and less on administrative tasks.
As medical record automation continues to evolve, the future holds exciting possibilities, including the integration of AI, machine learning, and blockchain technology. These advancements will only further improve the accuracy, security, and accessibility of medical records, enhancing the overall healthcare experience for both patients and providers.
Despite the challenges involved in implementing EHR system automation, the benefits far outweigh the obstacles. As more healthcare providers adopt automated medical record systems, the healthcare industry will continue to become more efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered, ultimately leading to better outcomes for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
EHR stands for Electronic Health Record, which is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart. It contains comprehensive patient information, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, test results, and more. Medical record automation refers to the process of automating the storage, retrieval, and management of these digital records. This automation reduces manual input, enhances accuracy, and ensures that healthcare professionals can access up-to-date, organized patient data efficiently. The integration of automated medical record systems within EHR frameworks makes healthcare operations smoother and safer for both patients and providers.
EHR automation streamlines healthcare processes by eliminating time-consuming paper-based record-keeping. It allows healthcare providers to quickly access comprehensive patient records, reducing the time spent searching for physical files. This leads to increased productivity, better management of patient information, and a faster response to medical needs. Furthermore, automated medical record systems can trigger alerts for missing or outdated information, ensuring that healthcare providers are always working with the most accurate data, thus minimizing the risk of errors and delays in patient care.
Automated medical record tracking systems help improve patient safety, streamline healthcare operations, and enhance communication among healthcare providers. By automatically logging every update to a patient’s medical record, these systems ensure accurate, real-time tracking of patient data. This makes it easy to retrieve the information when needed and reduces the chances of errors such as lost or misplaced records. These systems also facilitate easier collaboration among multiple healthcare providers by ensuring that each professional has access to the same up-to-date information, improving the quality and coordination of care.
The adoption of medical record automation can be challenging due to the high upfront costs of purchasing the required hardware and software. Smaller healthcare practices may find it difficult to finance such transitions. Additionally, staff must be properly trained to use the new automated systems, which can take time and resources. Another challenge is ensuring that different automated medical record systems are compatible with each other for seamless data sharing between healthcare organizations. Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits of EHR system automation—including improved efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings—usually outweigh the initial obstacles.
Medical record automation significantly improves patient care by ensuring that healthcare providers have immediate access to accurate, complete, and up-to-date patient information. With automated medical record systems, clinicians can quickly view a patient’s medical history, allergies, medication lists, and test results, leading to faster, more informed decision-making. Automation also helps prevent medication errors, missed diagnoses, and delays in treatment by providing alerts for critical information. This allows for safer, more effective patient care, as all the necessary data is readily available when needed.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize medical record automation in the future. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data to detect patterns and predict potential health risks before they arise. For instance, AI can flag abnormal lab results or suggest treatment options based on historical data. ML, on the other hand, continuously learns from new data, improving the accuracy and efficiency of automated medical record systems over time. Together, these technologies will enable more proactive healthcare, enhance diagnostic accuracy, and ultimately improve patient outcomes by offering personalized care recommendations based on the patient’s medical history.
Recent Articles
Table of Content 1. What is Staff Augmentation for App...
Table of Content 1. What is IT Staff Augmentation? 2....
Table of Content 1. The Role of IT Staff Augmentation...












