
Electronic Health Record system – a healthcare tool that’s in the spotlight! . Every healthcare organization today is beginning to leverage this ground-breaking technology to elevate patient care and every patient is leveraging this technology to ease their medical journey. For a tool like this that caters to a broader audience from different educational backgrounds, the interface has to be extremely accommodating and dynamic. This blog will let you explore the strategies for building an user-friendly EHR interface that will give a seamless user experience for patients, medical practitioners and other healthcare professionals.
What is EHR? How is it different from EMR?
An EHR (Electronic Health Record) is a comprehensive digital record of patients that generally comprises features like – Patient Demographics, Medical History, Medication Management, Allergy Information, Clinical Notes, Lab and Test Results, Treatment Plans, Patient Portals, Billing and Insurance Management, & Interoperability. It facilitates coordinated care and helps in enhancing overall quality of healthcare!
EMRs are designed to improve the workflow within a practice by storing patient information, including: Medical history Medication lists Allergies Lab results
Both EHRs and EMRs play critical roles in modern healthcare by digitizing patient records, improving access to information, but they have distinct characteristics and purposes.
EMRs are generally not designed for sharing patient information outside the practice. They lack interoperability in healthcare, making it difficult to transfer records to other healthcare providers.EHRs are designed to be interoperable, allowing for easier sharing of patient information between different healthcare organizations, which is essential for coordinated care.
Related reading : How to Build an EHR System: A Comprehensive Guide
What is an EHR interface?

An EHR interface refers to design, layout, navigation and other visual and functional elements in EHR that healthcare providers and patients interact with. Here are the key components of an EHR interface:
1. Dashboard: A central overview screen that displays key patient information, alerts, reminders, and quick access to frequently used features.
2. Patient Records: Sections that allow users to view and input comprehensive patient data, including medical history, medications, lab results, and progress notes.
3. Navigation Menus: Clear, organized menus that guide users through different sections of the EHR, such as scheduling, billing, and other clinical documentation.
4. Data Entry Forms: Structured forms for filling patient information, treatment plans, and clinical notes.
5. Search Functionality: Tool that allows users to quickly find patient records, or specific information within the system.
6. Alerts and Notifications: Real-time alerts for critical updates, such as appointment confirmation, appointment reminders, and other important information.
7. Patient Portal Integration: Features that connect with patient portals, enabling patients to access their health information, schedule appointments, and communicate with providers.
8. Reporting Tools: Options for generating reports and analytics on patient outcomes, practice efficiency, and compliance with healthcare regulations.
9. Collaboration Features: Tools for communication between healthcare providers, including messaging systems or shared notes, to enhance care coordination.
10. Customization Options: Settings that allow users to personalize their interface, including dashboard layouts, preferred workflows, and notification preferences.
Looking to create a simple yet effective EHR interface? Get in touch with Expert designers at Zazz!
Related reading : Top 5 Healthcare Mobile App Features
Why is it important to design simple EHR interfaces?
A simple, user-friendly interface helps healthcare providers access information quickly, leading to better patient care, and is crucial for improving user experience, enhancing efficiency, and reducing errors.
A simple user interface (UI) is significant for several reasons:
- User Experience: A clear and intuitive UI enhances user satisfaction by making navigation easier, reducing frustration, and allowing users to easily explore and get what they were looking for.
- Better Accessibility: Simplicity ensures that a wider range of users, including those with varying levels of tech literacy and those with disabilities, can access and use the interface effectively.
- Learning Curve: A straightforward UI minimizes the time needed for users to learn how to use the system, leading to quicker adoption and productivity.
- Reduced Errors: Simplified interfaces can lead to fewer errors, as users are less likely to become confused or overwhelmed by complex options.
- Consistency: A simple and consistent UI in cross applications fosters familiarity, making it easier for users to adapt from one interface to another.
- Effective interaction: Streamlined designs often lead to faster interactions, as users can take action with fewer clicks or inputs.
15- Key principles to build user-friendly EHR interface
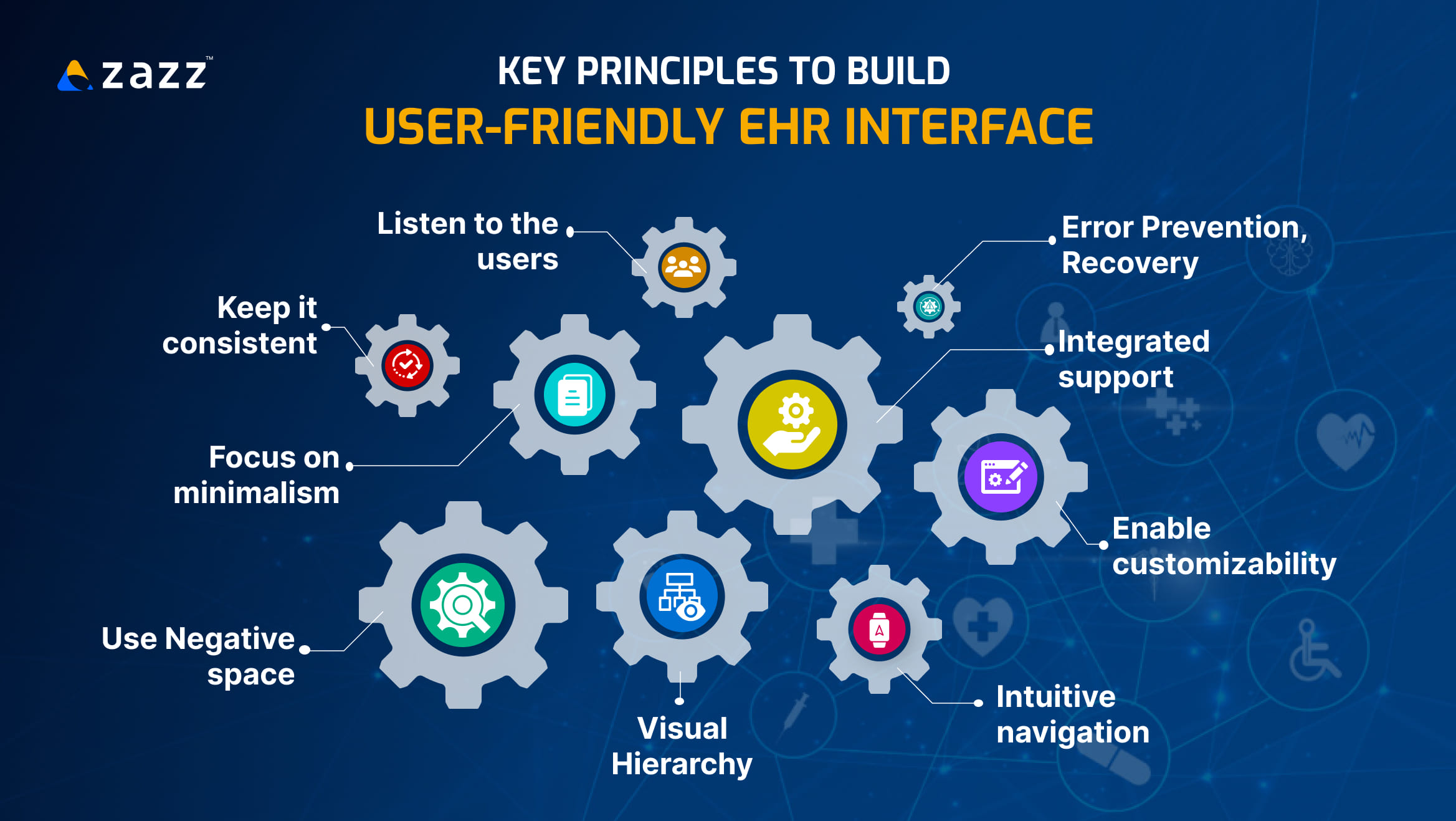
Understanding EHR design principles is quite crucial to build a user-friendly EHR system, as it not only involves medical professionals but also admin staff & patients from various educational backgrounds. Careful consideration of the following principles will help build a rewarding EHR interface that can greatly improve patient care & streamline operations.
- Listen to the users: Involve healthcare providers—doctors, nurses, and administrative staff—in the design process. Understanding their workflows and challenges will help create a system tailored to their needs, resulting in a more intuitive user experience.
- Keep it consistent: A consistent layout across the EHR platform is crucial. Use uniform terminology, colors, and design elements to create a familiar environment. This reduces the learning curve and helps users navigate the system more effectively.
- Focus on minimalism: Clutter can overwhelm users and hinder their ability to focus. A minimalist design emphasizes essential information and features, reducing distractions.
- Use Negative space: Use white space effectively to create a clean and organized interface.
- Make it mobile responsive: With the increasing use of mobile devices, a mobile responsive design is essential. Ensure that the EHR interface works seamlessly across all mobile devices, allowing users to access patient information on-the-go.
- Visual Hierarchy is key: Establishing a clear visual hierarchy helps users spot and distinguish. Use size, color, and spacing to highlight important data and actions. This guides users’ attention and makes it easier to locate critical information quickly.
- Error Prevention and Recovery: Design workflows that minimize the potential for errors. Implement features like dropdown menus, auto-fill, and validation checks. Additionally, when errors occur, provide clear and actionable messages to help users recover quickly.
- Enable customizability: Allowing users to customize their dashboards and workflows enhances usability. Personalized interfaces enable healthcare providers to prioritize the information and tools most relevant to their practice, improving overall efficiency.
- Meet accessibility standards: Ensure that the EHR interface meets accessibility standards (e.g., WCAG) to accommodate users with disabilities. This includes features like text-to-speech, keyboard navigation, and adjustable font sizes, making the system usable for everyone.
- Intuitive navigation: Organizing information logically is key to intuitive navigation. Ensure that menus and features are easy to locate and access. Implement breadcrumb trails, clear labels, and logical groupings to guide users through the interface effortlessly.
- Have integrated support: Provide context-sensitive help and easy access to user guides or tutorials directly within the interface. This support can empower users to troubleshoot issues independently, enhancing their experience and confidence in using the system.
- Include data visualization: Complex data can be challenging to interpret. Use charts, graphs, and dashboards to present data visually. This makes it easier for users to grasp trends and insights quickly, aiding in decision-making.
- Be open to iterations: Establish a continuous feedback loop with users to gather insights and make ongoing improvements to the interface based on their experiences.
- Include search tool: Implement advanced search capabilities to help users quickly locate patient records, clinical data, and relevant information.
- Integrate AI assistant: Sometimes the simplest navigation can be hard in complex situations, in which case an AI assistant can help users navigate easier and help them find what they are looking for in no time.
A well-designed EHR can significantly improve clinician satisfaction, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. By incorporating these principles, EHR systems can significantly enhance usability, ultimately leading to better patient care and clinician satisfaction.
Related reading : How can AI help reduce readmissions?
Need assistance to build your EHR system? Get expert guidance from Zazz- your reliable app development company|
5 User-friendly EHR apps to take notes from :

1. Epic Systems
Overview
Epic Systems is one of the largest EHR vendors in the U.S., widely adopted by hospitals and healthcare organizations.
User-Friendly Features
- Customizable Dashboards: Users can personalize their home screens with widgets for quick access to frequently used tools and information.
- Streamlined Navigation: Epic’s interface allows for intuitive navigation with a consistent layout, making it easy for users to find what they need.
- Mobile Access: The Epic Haiku and Canto apps provide mobile access, enabling providers to view patient information and communicate with staff on-the-go.
Benefits: The combination of a customizable interface and robust mobile capabilities ensures that healthcare providers can access and manage patient data efficiently, whether at the office or in the field.
2. Athenahealth
Overview
Athenahealth offers a cloud-based EHR solution that focuses on integrated billing, patient engagement, and population health.
User-Friendly Features
- Intuitive User Interface: The application is designed with a clean and simple layout, minimizing clutter and making it easy for users to navigate.
- Smart Calendar: An integrated scheduling feature helps manage appointments effectively, with reminders and follow-ups for patients.
- Patient Portal: Athenahealth’s portal allows patients to schedule appointments, access test results, and communicate with providers easily.
Benefits: With its focus on user experience and integrated features, Athenahealth enhances both provider efficiency and patient satisfaction, creating a more holistic healthcare experience.
3. Cerner
Overview
Cerner is another leading EHR provider known for its comprehensive suite of healthcare solutions.
User-Friendly Features
- Intuitive Workflow Design: Cerner’s interface supports a logical workflow, allowing users to move seamlessly between tasks.
- Real-Time Analytics: Built-in analytics tools help providers make informed decisions based on up-to-date patient data.
- Mobile-Friendly Options: Cerner’s solutions include mobile applications that empower healthcare providers to access critical information anytime, anywhere.
Benefits : Cerner’s focus on workflow optimization and real-time data access improves the efficiency of healthcare teams, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
4. Practice Fusion
Overview
Practice Fusion is a cloud-based EHR system designed primarily for small to medium-sized practices.
User-Friendly Features
- Simple Setup and Usability: The application is easy to set up and navigate, requiring minimal training for new users.
- Automated Patient Reminders: Practice Fusion automates reminders for appointments and follow-ups, reducing no-show rates.
- Integrated e-Prescribing: The e-prescribing feature streamlines medication management and helps avoid prescription errors.
Benefits: With its emphasis on ease of use and automation, Practice Fusion allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care rather than administrative tasks.
5. DrChrono
Overview
DrChrono is a versatile EHR platform designed for various specialties, offering robust customization options.
User-Friendly Features
- Fully Customizable Templates: Users can create tailored templates for their specific practice needs, enhancing documentation efficiency.
- Integrated Billing: The platform combines EHR with billing and practice management features, simplifying the financial aspects of healthcare.
- Patient Engagement Tools: DrChrono includes features like appointment reminders and patient check-in to improve engagement.
Benefits: DrChrono’s customizable nature and integrated features make it a popular choice among practitioners looking for a personalized approach to their EHR system.
The user-friendly EHR applications highlighted above are designed to simplify workflows, enhance communication, and improve overall patient care. As technology continues to evolve, investing in an intuitive EHR solution will be crucial for healthcare providers aiming to navigate the complexities of modern healthcare.
Related reading : Software Architecture for Healthcare Apps
Want to build an effective EHR app? Talk to app development experts at Zazz|
Conclusion:
Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems have revolutionized the way healthcare providers manage patient information. However, the effectiveness of these systems heavily relies on their usability. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, prioritizing user-friendly design in EMR/EHR systems will be essential in fostering a more efficient, responsive, and compassionate healthcare environment. By embracing these key principles, you can build an efficient EHR app that helps healthcare providers to deliver the best possible care, ensuring that technology serves as an ally in their mission to improve patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Effective EHR design principles include user-centered design, interoperability, data integrity, usability, flexibility, and security. These principles ensure that EHR systems meet the needs of healthcare providers while maintaining patient safety and data confidentiality.
User-centered design focuses on understanding the needs and workflows of end-users, such as clinicians and administrative staff. By involving users in the design process, EHRs can be tailored to support their tasks, reducing errors and improving overall efficiency and satisfaction.
Interoperability allows different EHR systems to communicate and share data seamlessly. This is crucial for providing comprehensive patient care, as it enables healthcare providers to access complete patient histories, lab results, and treatment plans from various sources, facilitating informed decision-making.
EHR design can ensure data integrity through robust validation processes and audit trails, which track changes and access to patient records. Security measures, such as encryption and user authentication, protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches.
Flexibility in EHR design allows for customization to meet the specific needs of different healthcare settings, specialties, and workflows. This adaptability enables providers to tailor the system to their practice, ensuring that it supports varied clinical processes and enhances user adoption.
Usability testing involves observing real users as they interact with the EHR system to identify pain points and areas for improvement. This feedback is essential for refining the interface, workflows, and features, ultimately leading to a more intuitive and efficient system that enhances user satisfaction and patient care.
Recent Articles
Table of Content 1. What is IT Staff Augmentation? 2....
Table of Content 1. What is Staff Augmentation for App...
Table of Content 1. What is IT Staff Augmentation? 2....












